Avicenna.AI partners UpCare for innovative value-based solutions to Canadian health providers

Avicenna.AI Partners With UpCare To Deliver Innovative Value-Based Solution to Canadian Health Providers
Viz.ai and Avicenna.AI Launch AI Care for Pulmonary Embolism & Aortic Disease

Viz.ai and Avicenna.AI Partner to Launch World-class AI-Driven Intelligent Care Coordination for Pulmonary Embolism and Aortic Disease
Avicenna.AI Joins Nuance AI Marketplace, Offering Cutting-Edge Solutions for Diagnostic Imaging

Avicenna.AI Joins Nuance AI Marketplace for Diagnostic Imaging for Stroke tools
AI triage solution for deadly vascular conditions receives FDA clearance and CE Mark
AI triage solution for Pulmonary Embolism and Aortic Dissection receives FDA clearance and CE Mark
Avicenna.AI receives CE Mark for stroke severity assessment AI tool
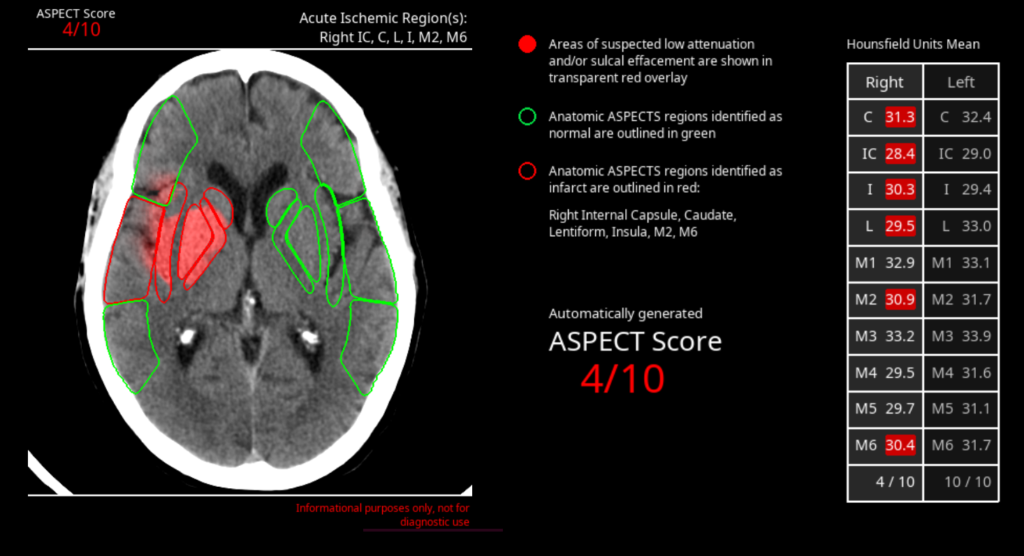
Avicenna.AI receives CE Mark for Automatic ASPECT Scoring AI tool
Dr. Jennifer Soun: Neuroscience to Radiology – Advancing AI in Clinical Practice

Dr. Soun is a board-certified UCI Health diagnostic radiologist who specializes in neuroradiology. Her clinical interests include stroke and vascular imaging.
Sur le marché de la radiologie, Avicenna.Ai se place en challenger
Installée à La Ciotat, cette entreprise offre aux radiologues un outil leur permettant de déterminer quels patients nécessitent une prise en charge d’urgence grâce à l’intelligence artificielle. Après avoir pris le temps de perfectionner sa solution, elle s’apprête à la mettre sur le marché et vise avant tout les États-Unis.
