Medical imaging AI company receives approval for algorithm enabling opportunistic detection and triage of vertebral compression fractures.
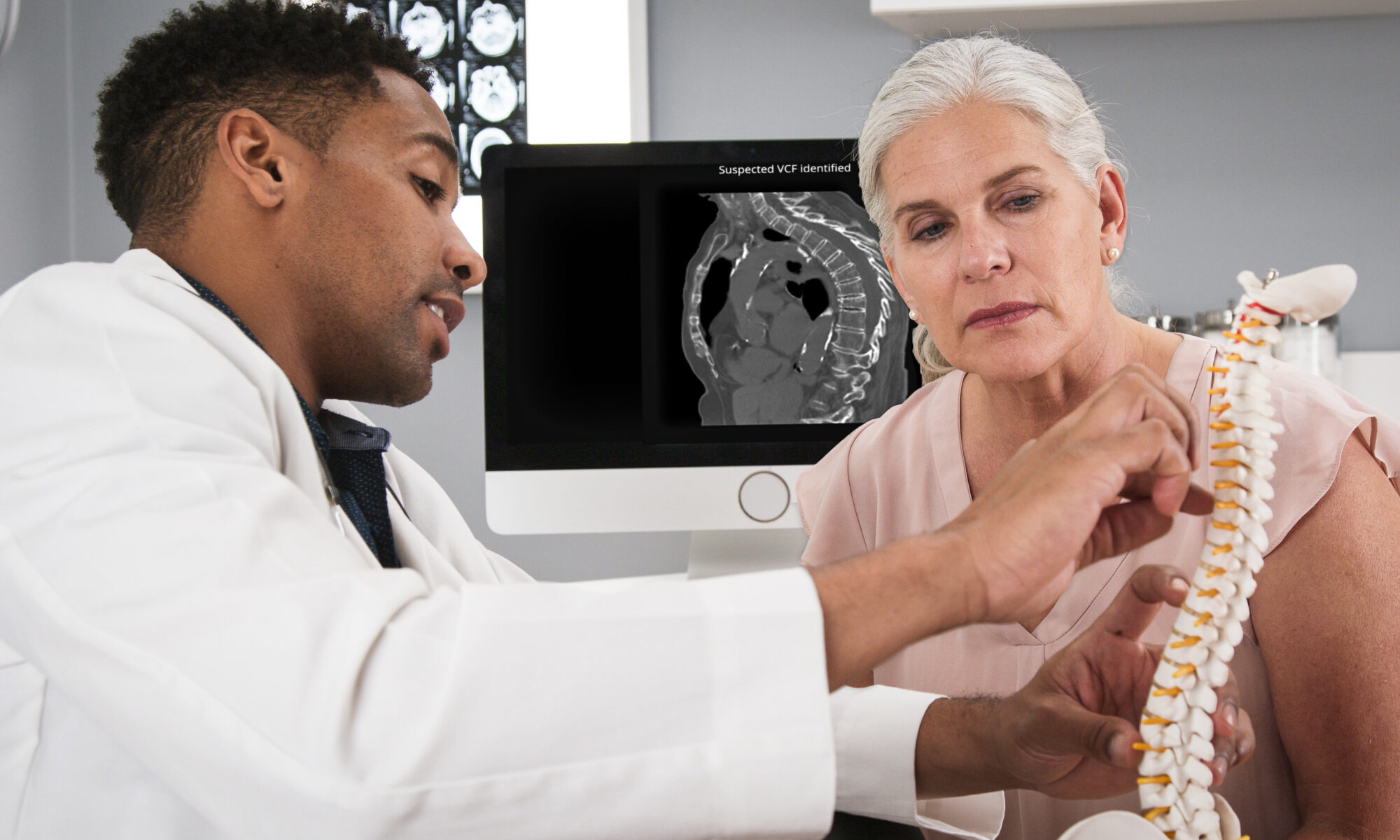
La Ciotat, FRANCE – June 12, 2024 – Avicenna.AI, a leading medical imaging AI company, has received 510(k) clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for CINA-VCF, a triage and notification AI tool that detects unsuspected vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) in patients undergoing chest or abdomen CT scans.
Often resulting from the deterioration of bone structure (osteoporosis), VCFs can cause significant pain, deformity, and height loss. In the USA, approximately 750,000 adults suffer from osteoporotic VCFs each year, but around two-thirds of those go undetected or unreported.
The CINA-VCF algorithm identifies and prioritizes vertebral compression fractures detected during routine CT scans for patients undergoing medical imaging for entirely different health conditions, notifying clinicians within seconds. The tool was validated on 474 CT scans (performed for other clinical indications than for VCF evaluation) acquired on 38 different scanner models from four different manufacturers, achieving excellent sensitivity and specificity results.
By facilitating the early detection of vertebral compression fractures, CINA-VCF aims to help prevent further bone density loss and additional fractures, enhancing patient care and outcomes. The tool enables vertebral fractures to be addressed before they multiply, reducing the risk of complications and potentially lowering medical expenses.
“Osteoporosis is a global burden affecting millions, especially postmenopausal women, and often goes unnoticed until symptoms like pain and loss of mobility appear,” said Cyril Di Grandi, co-founder and CEO of Avicenna.AI. “By detecting vertebral compression fractures early, we aim to help patients maintain better mobility and independence, enhance the well-being of those at risk, and reduce the burden on healthcare systems worldwide. We have also partnered with the International Osteoporosis Foundation to increase awareness about this debilitating condition.”
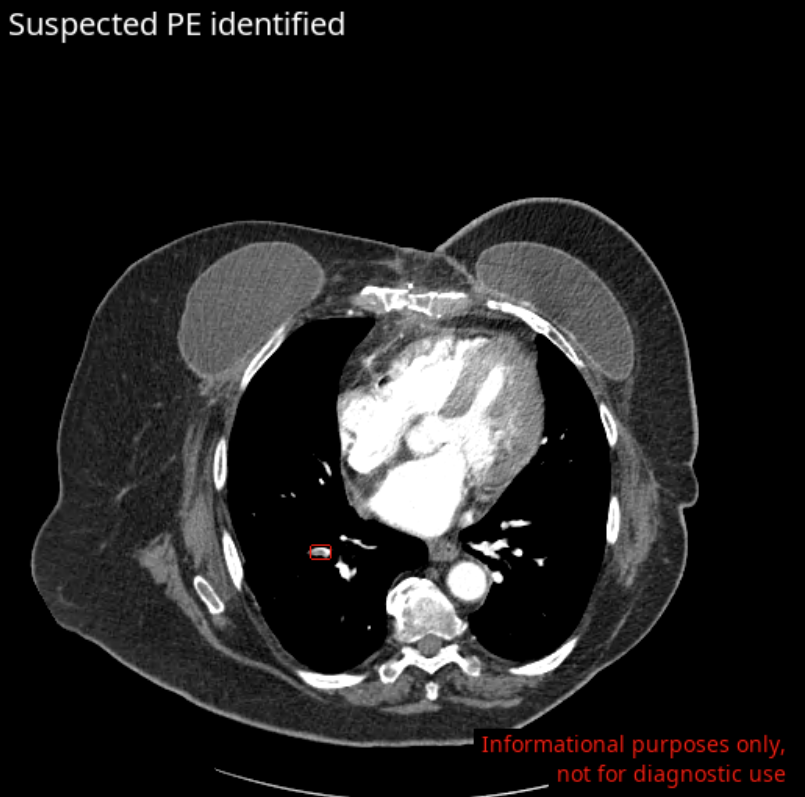
CINA-VCF is the latest tool from Avicenna.AI to secure FDA clearance, joining its AI solutions for automatic detection of a host of conditions from CT imaging. It is also the company’s second tool FDA-cleared for incidental findings, alongside CINA-iPE, which identifies unsuspected cases of pulmonary embolism in oncology patients.
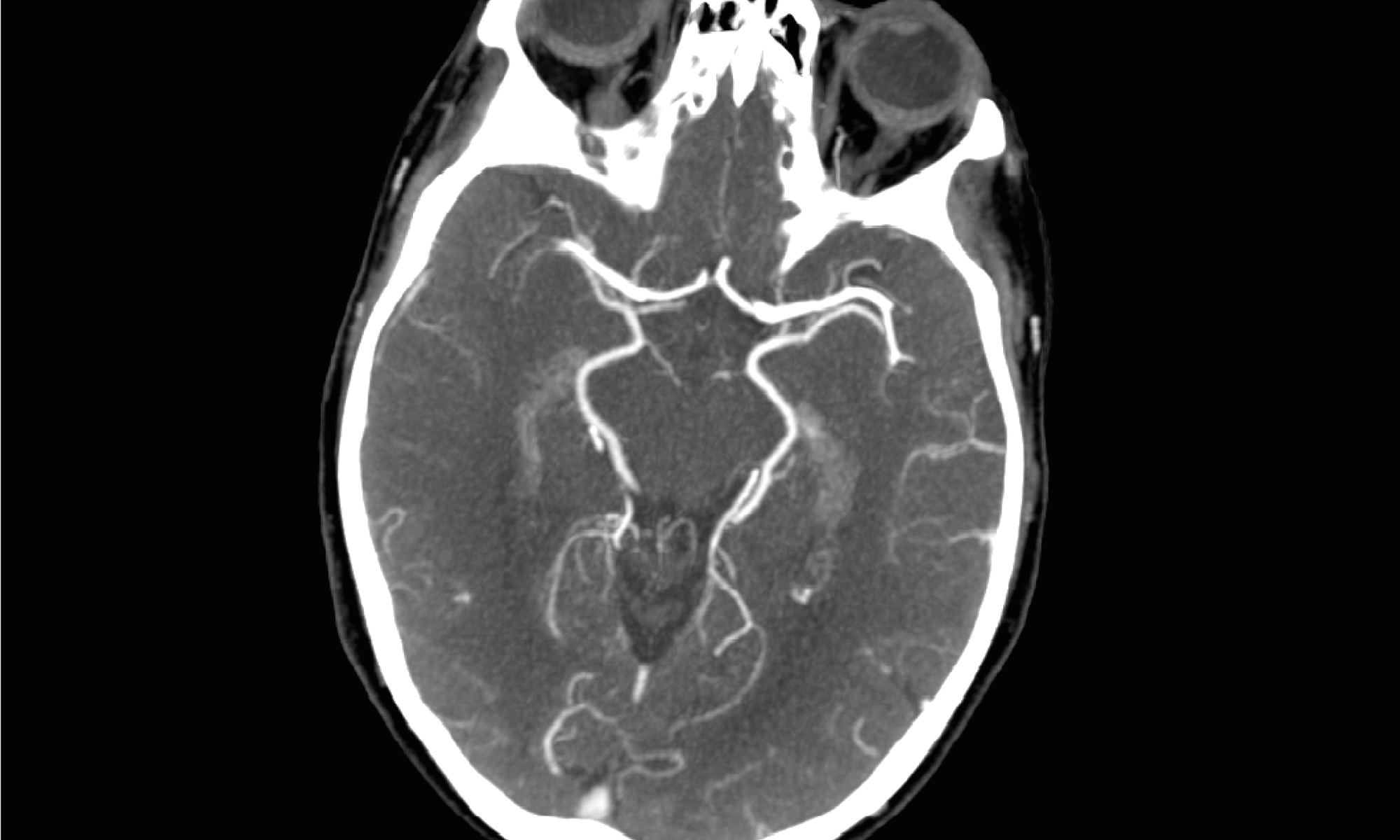
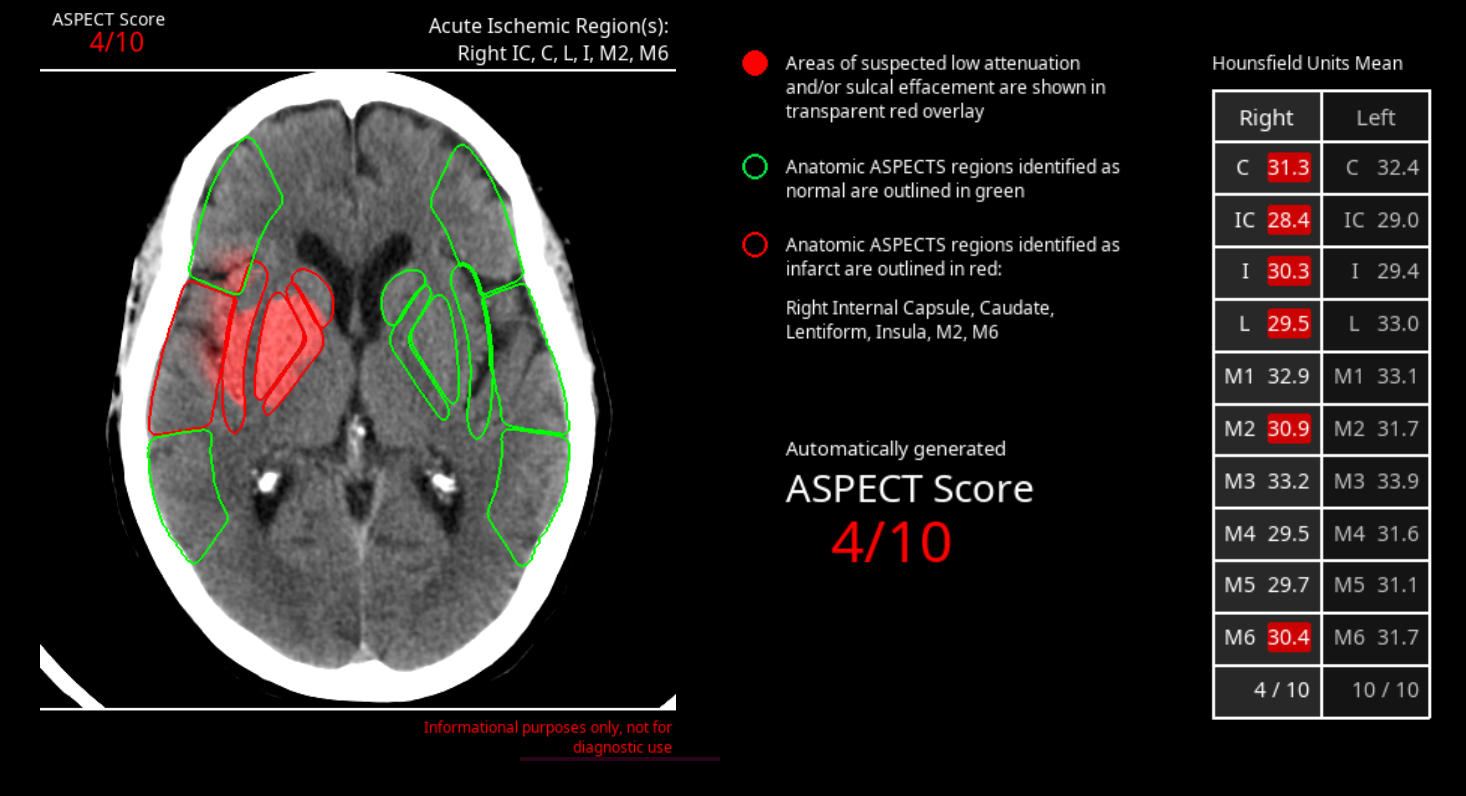
The company’s other AI tools include algorithms for intracranial hemorrhage (CINA-ICH), large vessel occlusion (CINA-LVO), aortic dissection (CINA-AD), pulmonary embolism (CINA-PE), and quantification of stroke severity (CINA-ASPECTS). All of Avicenna.AI’s AI tools are seamlessly integrated into radiologists’ clinical workflow, automatically triggering and reporting algorithm results through the systems already used by radiologists