Avicenna.AI is specialized in developing cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) solutions tailored for emergency radiology and incidental findings detection on CT scans. By seamlessly automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, Avicenna.AI liberates medical professionals to concentrate their expertise on cases of utmost urgency, thus facilitating quicker and more precise diagnoses.
 Intracranial Hemorrhage
Intracranial Hemorrhage
 ASPECT Score
ASPECT Score
 Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary Embolism
 Aortic Dissection
Aortic Dissection
 Incidental Pulmonary Embolism
Incidental Pulmonary Embolism
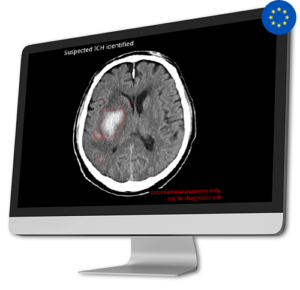 AI Tool for Automatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection
AI Tool for Automatic Intracranial Hemorrhage DetectionIntracranial hemorrhages (ICH) impact over two million individuals worldwide, with a high patient mortality rate of 40-50% within one month and 80% disability despite aggressive care. Early and precise diagnosis of ICH is crucial for prompt therapeutic responses and improved outcomes.
CINA-ICH is able to detect suspected intracranial hemorrhage on Non-Contrast CT Scan, significantly reducing turnaround time for head trauma injuries, and hemorrhagic stroke patients.
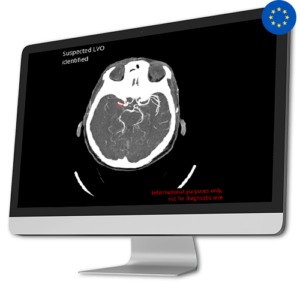 AI Tool for Automatic Large Vessel Occlusion Detection
AI Tool for Automatic Large Vessel Occlusion DetectionApproximately 80% of all strokes are caused by Ischemic stroke due to a Large Vessel Occlusion (LVO).
Early diagnosis of LVO is crucial as every 10 minutes of delay can significantly impact the patient’s disability outcome.
CINA-LVO swiftly detects LVO in the anterior circulation (distal ICA, M1, or proximal M2) on head CT angiographies and prioritizes these cases in the radiologist’s worklist.
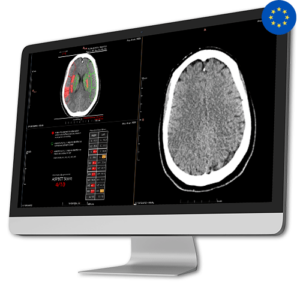 AI Tool for Automatic ASPECT Scoring
AI Tool for Automatic ASPECT ScoringCINA-ASPECTS, an AI-based quantification tool, facilitates faster, more consistent, and precise assessment of acute ischemic stroke. Besides the ASPECT Score, CINA-ASPECTS offers: a heat map indicating the probability of hypodensity and/or sulcal effacement, outlines infarcted regions, and a summary chart with mean Hounsfield Unit per region.
The ASPECTS (Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score) is a scoring system to assess the evaluation of ischemic stroke cases eligible for mechanical thrombectomy and/or intravenous thrombolysis (IVT).
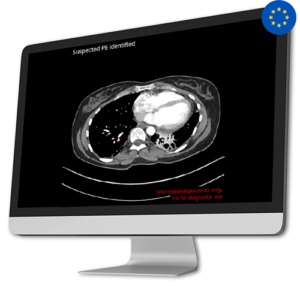
 AI Tool for Automatic Pulmonary Embolism Detection
AI Tool for Automatic Pulmonary Embolism DetectionPulmonary embolism is a substantial global health concern, responsible for a significant number of fatalities, illnesses, and hospital stays across the globe. The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is complex due to its diverse array of manifestations, clinical signs lacking specificity, and the possibility of resembling other medical conditions.
In response to this critical issue, Avicenna.AI developed CINA-PE, a cutting-edge solution that swiftly and automatically detects pulmonary embolism from chest CT Scan.
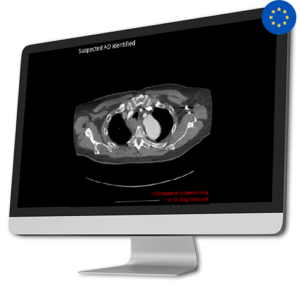 AI Tool for Automatic Aortic Dissection Detection
AI Tool for Automatic Aortic Dissection DetectionAortic Dissection is a very serious and potentially life-threatening condition. Detecting it promptly is extremely important, as time is crucial for better outcomes. To meet the urgent need for quicker diagnosis and treatment, CINA-AD identifies acute type A and B aortic dissections that need immediate medical attention.
By helping healthcare professionals quickly identify and prioritize these cases, CINA-AD gives real-time and precise alerts during thoraco-abdominal angiography. This guarantees that patients get fast access to the required treatment and intervention, greatly increasing their chances of recovery.
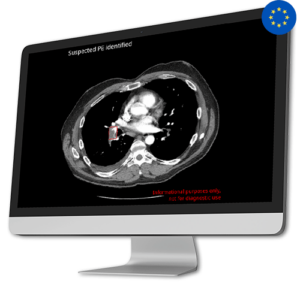
 AI Tool for Automatic Off Search Pulmonary Embolism Detection
AI Tool for Automatic Off Search Pulmonary Embolism DetectionWith CINA-iPE, healthcare professionals can detect Lung blood clots in patients undergoing imaging for other potential health issues, especially those with suspected oncological conditions.
Focused on Incidental Findings, CINA-iPE plays a crucial role in enhancing follow-up procedures and ultimately improving patient outcomes. CINA-iPE identifies lung blood clots in various types of CT scans that cover at least the lower lung area. These scan types include full-body scans, scans of the chest, abdomen and pelvis, and scans of the thoracic area along with the abdomen and pelvis.

At Avicenna.AI, our AI-based tools are designed to expedite disease detection processes, providing swift and accurate results. Leveraging advanced technologies and algorithms, our tools empower healthcare professionals to identify conditions promptly, ensuring timely intervention and treatment.

Efficient patient management is crucial in delivering high-quality healthcare. With Avicenna.AI’s solutions, healthcare professionals can streamline patient workflows, prioritize critical cases, and allocate resources effectively. This optimization leads to improved patient outcomes and enhanced overall healthcare efficiency.
With our AI tools handling routine tasks, radiologists can process a larger volume of cases within a shorter timeframe. This increased productivity helps radiology departments handle growing workloads, reduce turnaround times, and enhance patient satisfaction by providing timely reports and interventions.
Don't miss the opportunity to take a leap into the future of radiology with us!

“In addition of being a high-performance software, Avicenna.AI gives access to patient results within 2 to 5 minutes, thus allowing radiologists to accelerate time of interpretation, providing a better service for our hospitals and better patient outcomes. The use of AI tools allows us to stay at the cutting edge of innovation which is key for our radiologist network and to remain effective 24/7.
Paul Cayot, Sales Director at Telediag

"What sets Avicenna.AI apart is the high accuracy of its algorithms and their impressive generalizability across multiple CT scanners. Moreover, their performance remains remarkable across various CT protocols, including different KV settings and both single and dual-energy CT protocols. This level of compatibility can help streamline workflow and enhance efficiency across an enterprise-level practice like ours."
Anonymous source - United States

“In a busy practice, radiologists are expected to interpret exams quickly and accurately. The Avicenna software solution provides an AI-assisted preliminary review of all exams, helping to prioritize patients with positive findings and optimize our clinical workflow. In addition, the extra "set of eyes" provided by the Artificial Intelligence software improves our overall confidence and efficiency.”
Daniel Chow, Radiologist, UC Irvine School of Medicine

“The main benefit of Avicenna.AI solution is that it’s a one-click solution. We don't have to get involved to place regions of interest or cursors. Everything is automated. While the images are processed by the CT scan, they are sent to an internal cloud at the same time. Then they automatically go to our PACS. It simply appears as an additional image with an alert in case of detected findings.”
Vincent Dousset, Head of Neuro-imaging, CHU Bordeaux